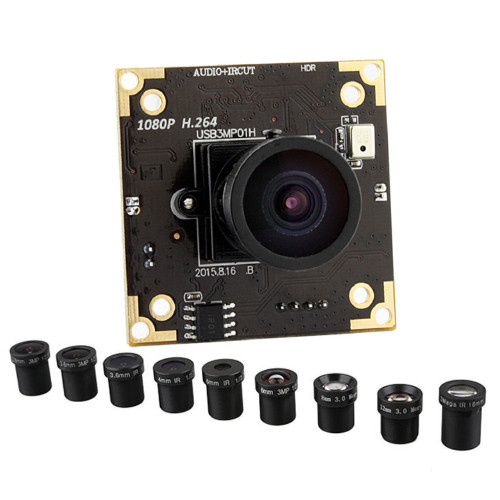
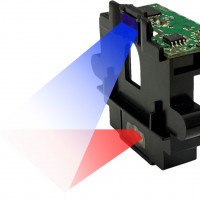
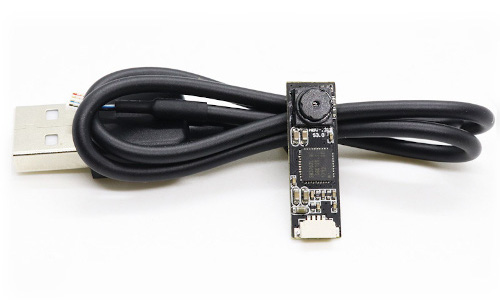
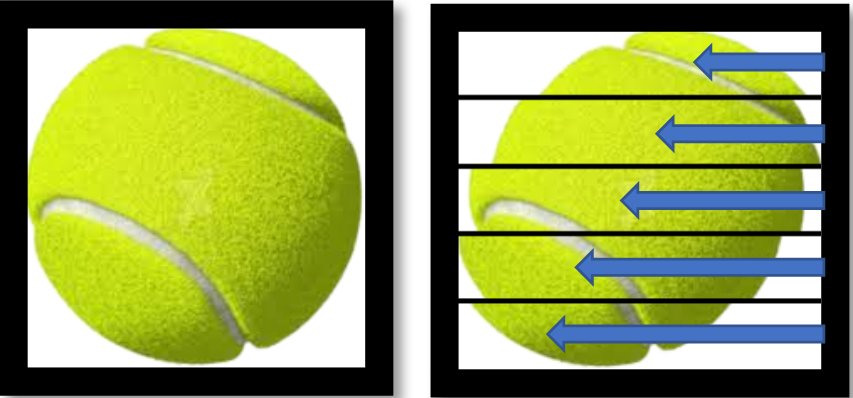
USB Camera Module
Brand: iAPhotonics
We collect M7 board lenses for board camera options, also support custom board lens as your requirements.
Here list the standard M7 board lenses for reference.
Product ID
FL(mm)
..
Starting From $3.0
Brand: iAPhotonics
We collect standard M12 camera lens module for options, also can customize camera lens module as your requirements.
Here list the standard M12 camera lens module for reference.
Prod..
Starting From $3.0
Brand: iAPhotonics
We collect M12 board camera lens for board camera options, also support custom board camera lens as your requirements.
Here list the standard M12 camera lens module for reference.
P..
Starting From $5.0
Brand: IADIY
CM03M30M5S is a VGA USB camera board using 1/7” GC0307 designed for low cost and small camera device applications. CM03M30M5S is a cost effect solution of small USB camera module for basic video camer..
$9.0
Brand: IADIY
CM03M120M5S is a VGA USB camera board using 1/6.5” GC0308 designed for cost effective and small camera. It is a functional and high frame rate solution of small USB camera module for monitoring and im..
$13.0
Brand: IADIY
CM2M30M5L slender USB camera module delivers low light sensitivity, good S/N ratio and dynamic range enabling camera module to detect in every lighting condition. It is an ideal solution for image sen..
$20.0
Brand: IADIY
CM2M30M7L slender USB camera module delivers low light sensitivity, good S/N ratio and dynamic range enabling camera module to detect in every lighting condition. It is an ideal solution for image sen..
$20.0
Brand: IADIY
CM5M30M5L camera sensor module delivers high resolution, good dynamic range enabling camera module to detect in every lighting condition. It is an ideal solution for video conference, face recognition..
$28.0
Brand: IADIY
CM5M30M7L camera sensor module delivers high resolution, good dynamic range enabling camera module to detect in every lighting condition. It is an ideal solution for video conference, face recognition..
$27.0
Brand: IADIY
CM8M15M5L USB latop camera board delivers high resolution, good dynamic range enabling camera module to detect in every lighting condition. It is an ideal solution for video conference, face recogniti..
$40.0
Brand: IADIY
CM03M60M12Q is a VGA USB board camera with good low-light performance. It has an ability to stream seamlessly at wide temperature range with S-mount M12 lens holder which allows customers to choose an..
$30.0
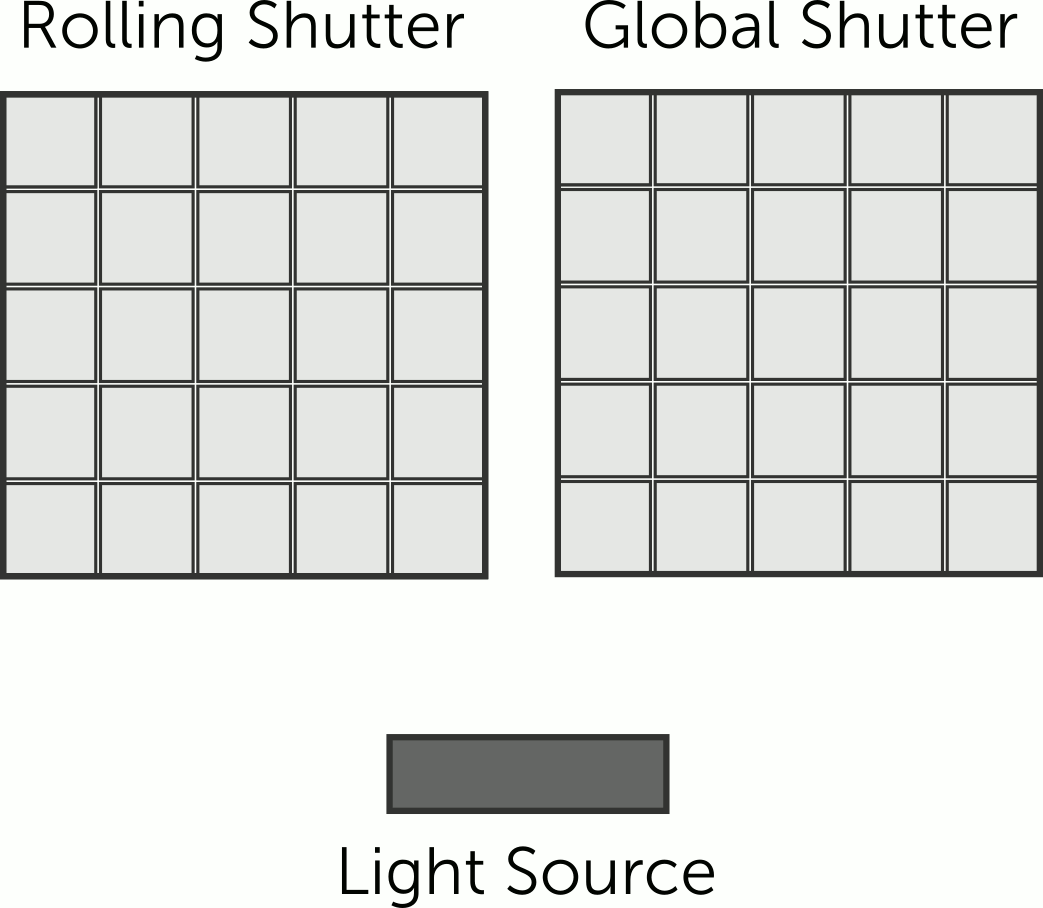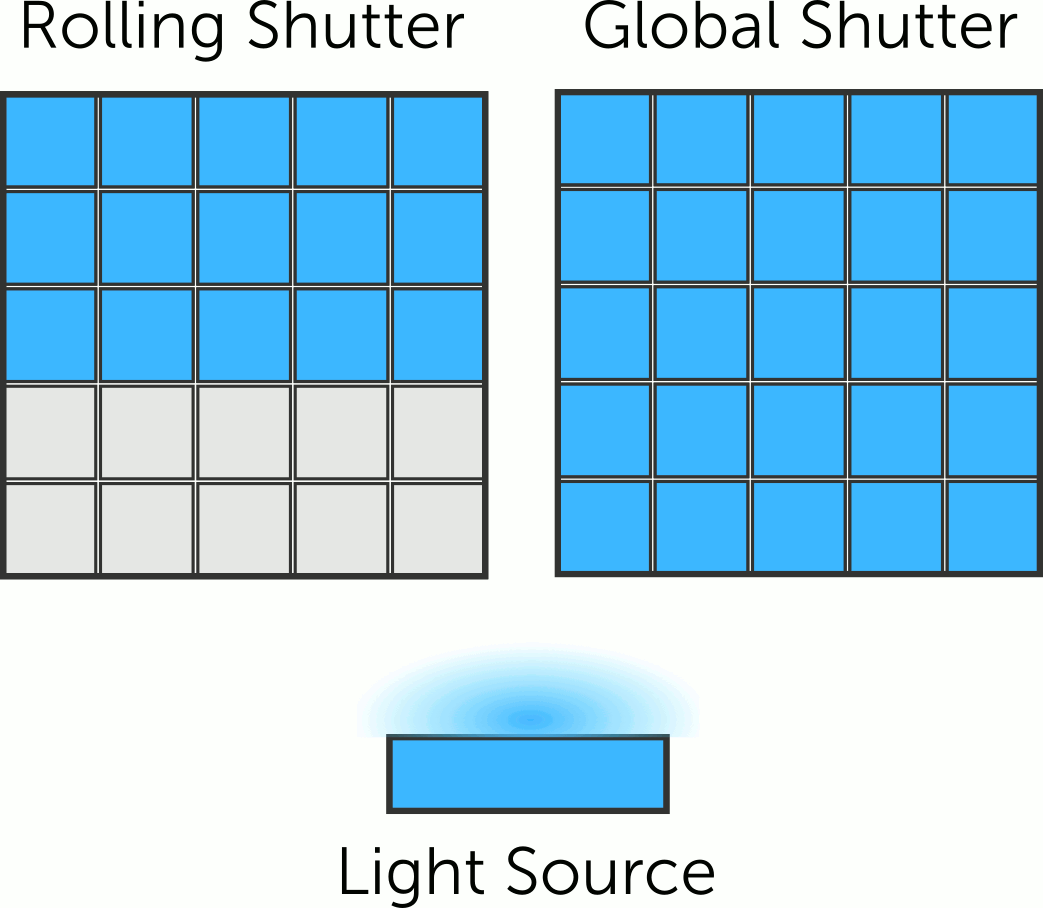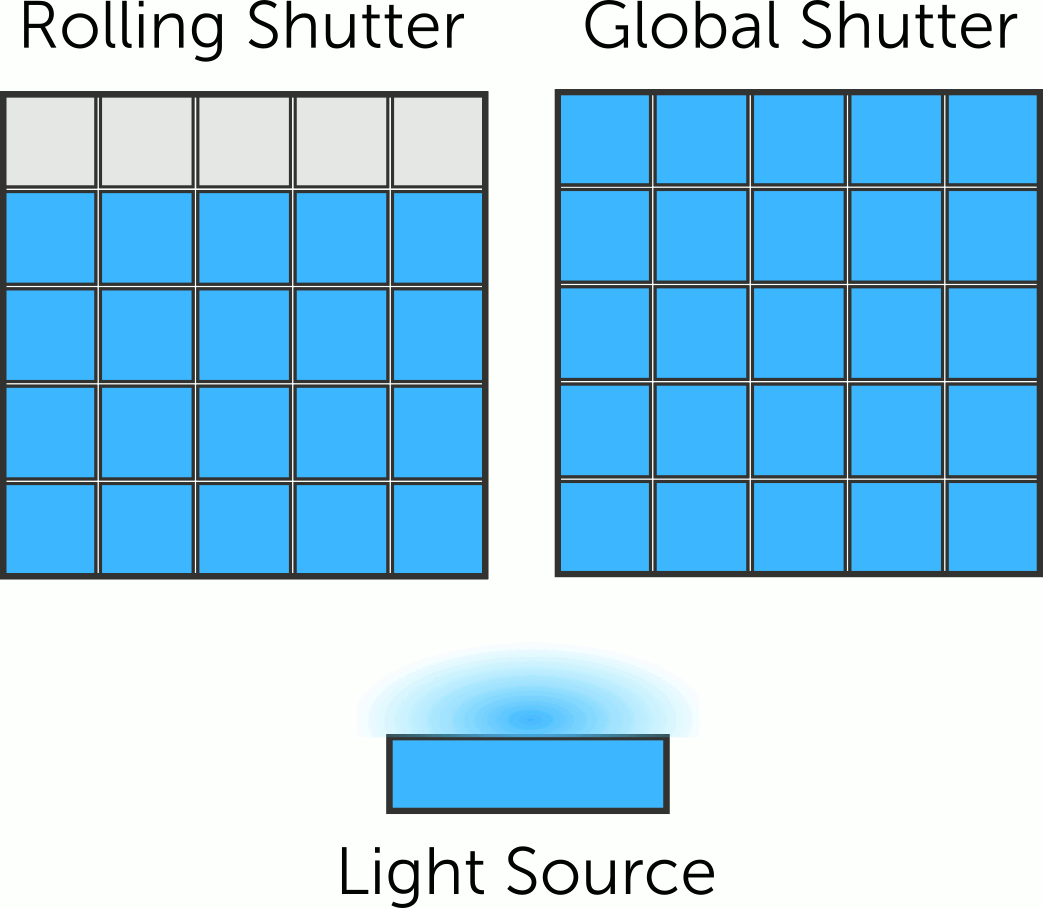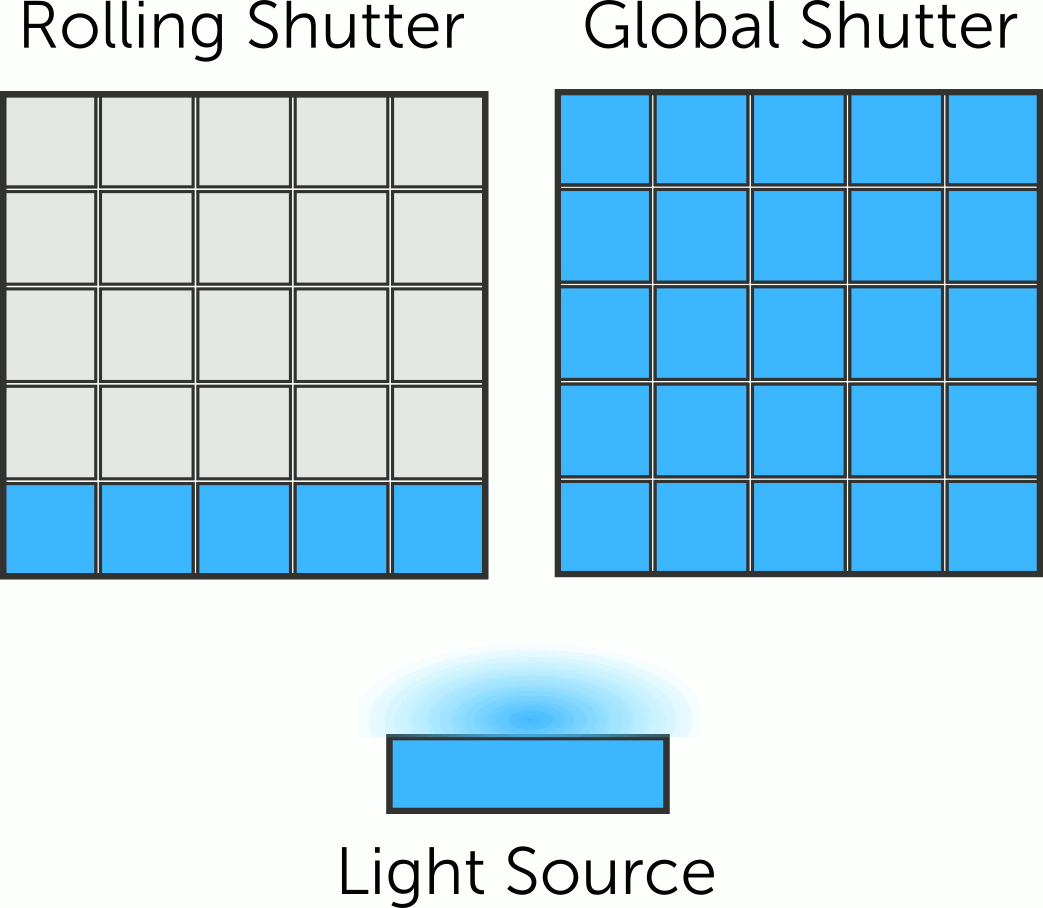
Brand: IADIY
CM03M180M12QG is a global shutter 180fps high frame rate USB board camera for action photography and machine vision. It is an ideal solution for security, automation, video conference, and portable me..
$35.0
Brand: IADIY
CM1.3M30M12Q is a 1.3 MP USB camera board using 1/3” AR0130 with superior low illumination and excellent performance. It is an ideal solution for Day/Night Vision Surveillance and NIR Imaging in IR im..
$40.0
Brand: IADIY
CM2M120M12Q delivers low light sensitivity, good S/N ratio of 40dB, and dynamic range of 69dB, enabling cameras to operate in every lighting condition. It is an ideal solution for security, camcorder,..
$52.0
Brand: IADIY
CM2M60M12QG is a global shutter high frame rate USB board camera for action photography and machine vision. It is an ideal solution for security, camcorder, video conference, and portable media video ..
$98.0
Brand: IADIY
CM3M30M12Q is a 3MP USB camera board using 1/3” AR0331 designed for both low light and high dynamic range scene performance. It is an ideal solution of WDR camera module for wide dynamic range applica..
$64.0
Brand: IADIY
CM5M30M12Q is a 5MP USB camera sensor module with anti-shake engine for the mobile device and still camera applications. As full function support, it is a cost effective solution of high performance v..
$70.0
Brand: IADIY
CM5M30M12Q2 is a 5MP USB camera sensor module with anti-shake engine for the mobile device and still camera applications. As full function support, it is a cost effective solution of high performance ..
$70.0
Brand: IADIY
CM5M50M12QG is a 5MP USB camera module with global shutter technology, designed to capture fast-moving objects with clear, distortion-free images. It offers high-quality performance for both video and..
$162.0
Brand: IADIY
CM8M30M12Q is a 8MP USB camera module for the industrial and biomedical microscope high resolution applications. As the full function support, it is a high performance industrial and high resolution d..
$80.0
Brand: IADIY
CM8M30M12Q3 is a 8MP Camera module for the industrial and biomedical microscope high resolution applications. As the full function support, it is a high performance industrial and high resolution digi..
$86.0
Brand: IADIY
CM8M30M12Q2 is a high-performance 8MP USB camera module featuring the Sony IMX415 CMOS sensor with HDR, high sensitivity, and low noise enabled by STARVIS™ technology.
Technical Information:..
$90.0
Brand: IADIY
CM8M60CQ is an 8MP (3840x2160) USB camera board featuring the IMX585 sensor. It delivers high dynamic range (HDR), ultra-low-light sensitivity, and low noise performance with STARVIS™ technology. Feat..
$480.0
Brand: IADIY
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table td {
padding: 2px 8px; /* Less padding for tighter spacing */
line-height: 1.2; /* Reduced line-height */
}
table tr {
ma..
$200.0
Brand: IADIY
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table td {
padding: 2px 8px; /* Less padding for tighter spacing */
line-height: 1.2; /* Reduced line-height */
}
table tr {
ma..
$370.0
Showing 1 to 25 of 25 (1 Pages)