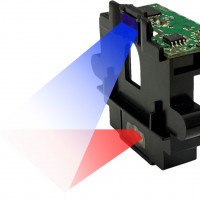
Laser Safety

- [What is laser safety?]
- [What is IEC60825-1 Standard?]
- [Laser Class 1]
- [Laser Class 1M]
- [Laser Class 2]
- [Laser Class 2M]
- [Laser Class 3]
- [Laser Class 3R]
- [Laser Class 4]
- [Related Video]
- [Reference]
What
is Laser Safety?
Since the first laser developed in 1964,
lasers have been used as an effective tool in a wide array of different
use cases, but this powerful light source can be dangerous if operated
improperly. Laser safety is the safe design, use and implementation of
lasers to minimize the risk of laser accidents, especially eye
injuries. Even relatively small amounts of laser light can lead to
permanent eye injuries, so the sale and usage of all lasers are subject
to government regulations. Laser safety can be divided into Class
1, Class 1M, Class 2, Class 2M, Class
3R(3A), Class 3B, Class 4. In the USA. it is considered that Class
1 to Class 3R(3A) lasers
are safe for consumers. In the EU,
laser products are required to be Class
1, Class 2, Class 1M, Class
2M for consumers products. While working
with class 3B and class 4 lasers, one must wear safety goggles which
are designed to absorb light of a particular wavelength.
As professional laser module manufacturer, IADIY standard laser modules all fit eye safety requirements and support customers to apply for FDA accession number.
Classification:
IEC60825-1 Standard
The classification of a laser is based on the concept of accessible emission limits (AEL) that are defined for each laser class. This is usually a maximum power (in W) or energy (in J) that can be emitted in a specified wavelength range, exposure time that passes through a specified aperture at a specified distance. Main characteristics and requirements for the classification system, specified by the IEC 60825-1 standard, is listed.
Laser
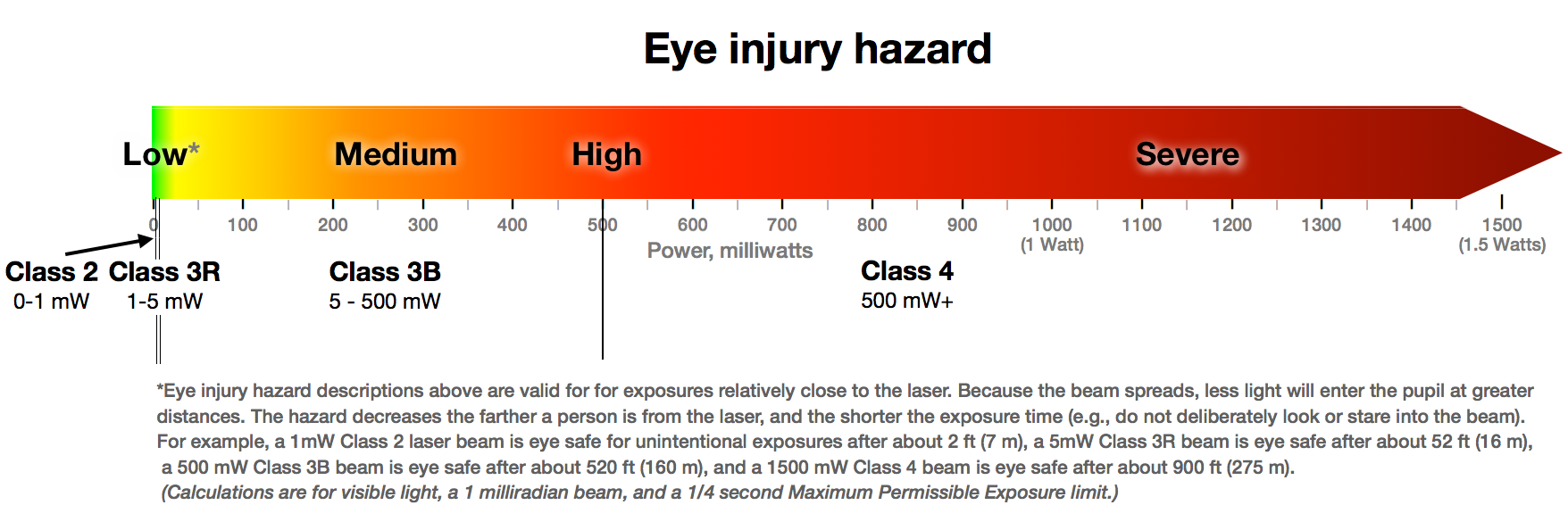
Class 1 (Class I) (Output Power <0.39mW through Dia. 7mm
Aperture @10cm Distance)
CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
Class 1 laser is safe under all conditions of normal use. This means the maximum permissible exposure (MPE) cannot be exceeded when viewing a laser with the naked eye or with the aid of typical magnifying optics (e.g. telescope or microscope). To verify compliance, the standard specifies the aperture and distance corresponding to the naked eye. For example, a high-power laser with a very large beam or highly divergent beam may be classified as Class 1 if the power that passes through the apertures defined in the standard is less than the AEL for Class 1. Often, devices such as optical drives will be considered class 1 if they fully contain the beam of a more powerful laser, such that no light escapes under normal use.
Laser Class 1M (for Divergent Laser, Output Power <0.39mW through Dia. 7mm Aperture @10cm Distance)
LASER RADIATION
DO NOT VIEW DIRECTLY WITH OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
CLASS 1M LASER PRODUCT
A Class 1M laser is safe for all conditions of use except when passed through magnifying optics such as microscopes and telescopes. Class 1M lasers produce large-diameterbeams, or beams that are divergent. The MPE for a Class 1M laser cannot normally be exceeded unless focusing or imaging optics are used to narrow the beam. A laser can be classified as Class 1M if the power that can pass through the pupil of the naked eye is less than the AEL for Class 1.
Laser Class 2 (Output Power <1mW)
LASER RADIATION
DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM
CLASS 2 LASER PRODUCT
A
Class 2 laser is considered to be safe but may cause eye strain if one
stares directly into the beam for a prolonged duration. This
classification is only available for lasers which use visible light
(400nm-700nm) thus it is not possible for infrared or ultraviolet
lasers to obtain Class 2 (or 2M) classification. Class 2 lasers are
limited to 1 mW continuous wave, or more if the emission time is less
than 0.25 seconds.
Laser Class 2M (for Divergent Laser, Output Power <1mW through Dia.7mm Aperture @10cm Distance)
LASER RADIATION
DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM OR VIEW
DIRECTLY WITH OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
CLASS 2M LASER PRODUCT
A
Class 2M laser is safe because of the blink reflex if not viewed
through optical instruments. As with class 1M, this applies to
laser beams with a large diameter or large divergence, for which the
amount of light passing through the pupil cannot exceed the limits for
class 2.
Laser Class 3R(3A) (Output Power <5mW)
LASER RADIATION
AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
CLASS 3R LASER PRODUCT
A
Class 3R laser is considered safe if handled carefully, with restricted
beam viewing. With a class 3R laser, the MPE can be exceeded, but
with a low risk of injury. Visible continuous lasers in Class 3R
are limited to 5mW. For other wavelengths and for pulsed lasers, other
limits apply.
Laser Class 3B (Output Power <0.5W)
LASER RADIATION
AVOID EXPOSURE TO BEAM
CLASS 3B LASER PRODUCT
A
Class 3B laser is hazardous if the eye is exposed directly, but diffuse
reflections such as those from paper or other matte surfaces are not
harmful. The AEL for continuous lasers in the wavelength range from
315 nm to far infrared is 0.5 W. For pulsed lasers between
400 and 700 nm, the limit is 30mJ. Class-3B lasers must be
equipped with a key switch and a safety interlock. Class 3B lasers
are used inside CD and DVD writers, although the writerunit itself is
class 1 because the laser light cannot leave the unit.
Laser Class 4
LASER RADIATION
AVOID EYE OR SKIN EXPOSURE TO
DIRECT OR SCATTERED RADIATION
CLASS 4 LASER PRODUCT
Class
4 is the highest and most dangerous class of laser, including all
lasers that exceed the Class 3B AEL. By definition, a class 4
laser can burn the skin, or cause devastating and permanent eye damage
as a result of direct, diffuse or indirect beam viewing. These lasers
may ignite combustible materials, and thus may represent a fire risk.
Class 4 lasers must be equipped with a key switch and a safety
interlock. Most industrial, scientific, military, and medical lasers
are in this category. Medical lasers can have divergent emissions and
require awareness of nominal ocular hazard distance (NOHD) and nominal
ocular hazard area (NOHA).
Related Video
Reference
More laser safety introduction: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laser_safety
IEC60825-1 : 2014 official link: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/3587
IEC60825-1edition1.2
reference: Download ![]()
FDA Accession number application:
Download ![]()






















































Leave a Comment