USB Camera Module
There are no products to list in this category.
The USB camera module is a general-purpose camera control board designed for both PCs and embedded systems like the ARM, Raspberry Pi, Odroid, and similar hardware. It supports almost all parallel interface image sensors and many MIPI camera sensors, including both global and rolling shutter sensors. The USB cameras adopt the standards of the USB interface, so they are easily expandable and adapted. What’s more, they could be made driver-free by following the USB device standards.

Different Camera Lens Optional
The UVC is one of the USB device classes. The drivers for UVC cameras to work have already been preinstalled in the operating system. Those driver-free USB cameras are UVC cameras. Computer and other mobile devices are connected directly through the USB interface — simply plug and play. These UVC compliant camera modules are compatible with Windows and Linux software and do not require drivers.
The USB camera module integrates the camera unit and the video capture unit, and then connects to the host system through the USB interface. The camera unit combining the camera lens to the image sensor depends on different image requirements like view angle, resolution, sensor features, etc. The video capture unit usually considers the image processing application: the filter which wavelength band we need, compatible DSP or microcontroller, sensor commands support, frame rate, etc. IADIY offers several UVC board cameras as an implement for our current embedded MIPI camera modules. These cameras have more case-specific features like Wide Dynamic Range (WDR), low light enhancement, and also different view angle camera lens optional.
More information please review camera sensor module introduction or custom camera module requirements flow.
An electronic shutter electronically turns the image sensor on and off to control exposure. The sensor starts detecting light when activated and stops detecting light when deactivated.
Rolling shutter cameras capture the scene line by line, from top to bottom, causing a time difference between top and bottom parts. Motion or camera movement results in the distortion known as the rolling shutter effect.
On the other hand, a global shutter camera is designed to capture an image by simultaneously exposing all the pixels in its image sensor to light for a brief period of time. Unlike a rolling shutter camera, which scans the image sensor row by row, a global shutter camera captures the entire image instantaneously.
Rolling shutter distortion is an effect that can occur while using rolling shutter cameras to capture fast-moving subjects. It is caused by the delay between the beginning and the end of the sensor readout. This can result in vertical or horizontal lines appearing bent or slanted, giving the image a distorted appearance.
More global shutter camera module information is available at camera sensor module introduction or custom camera module requirements flow.
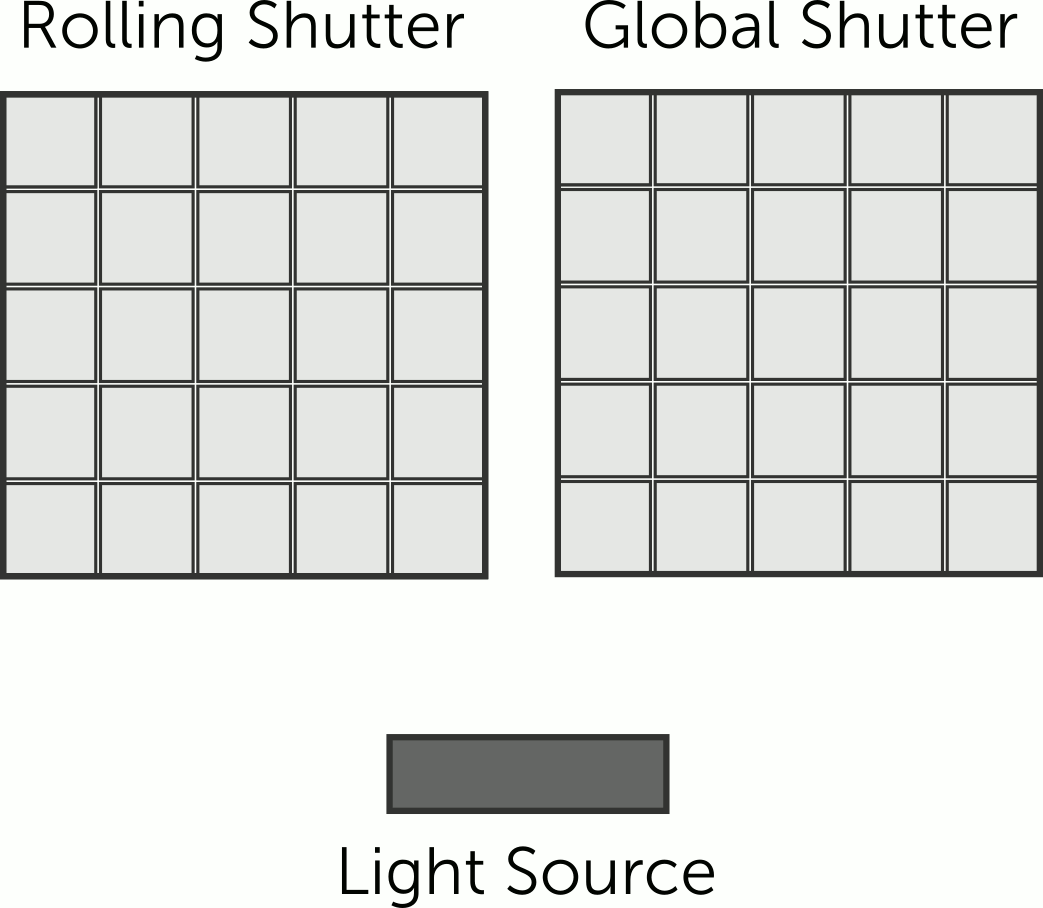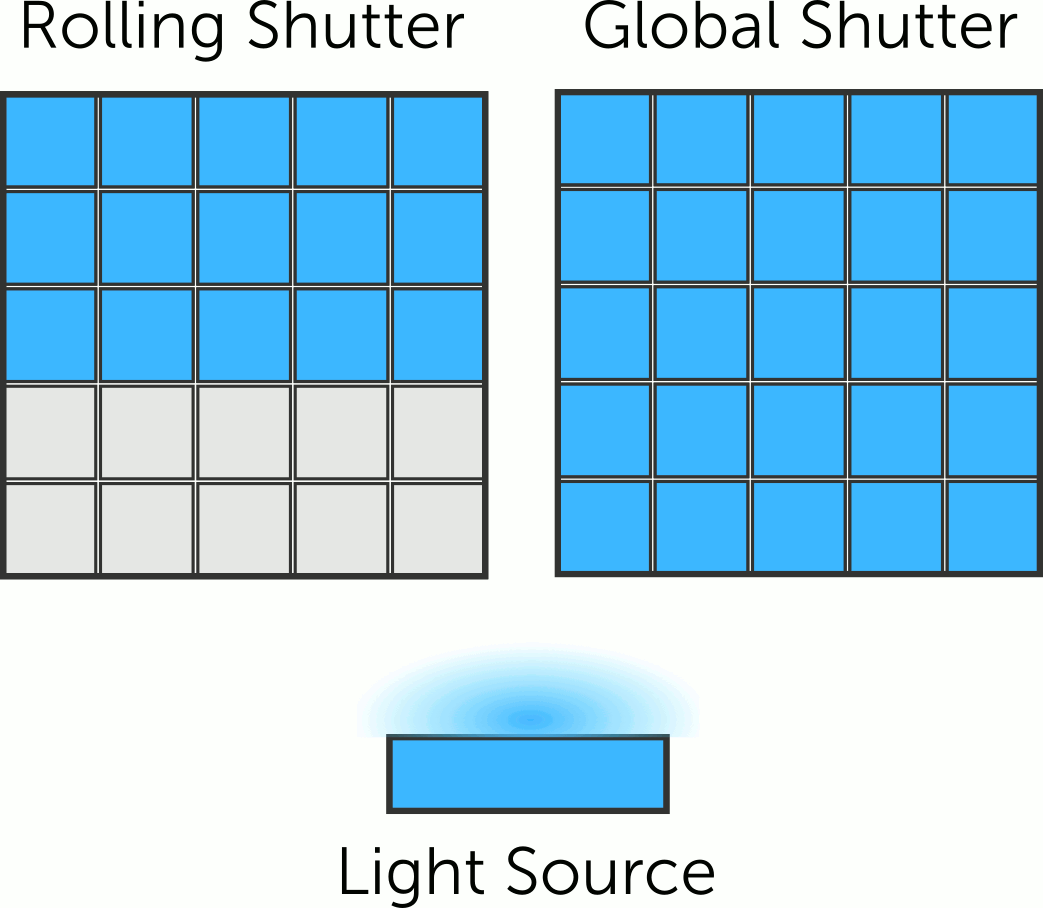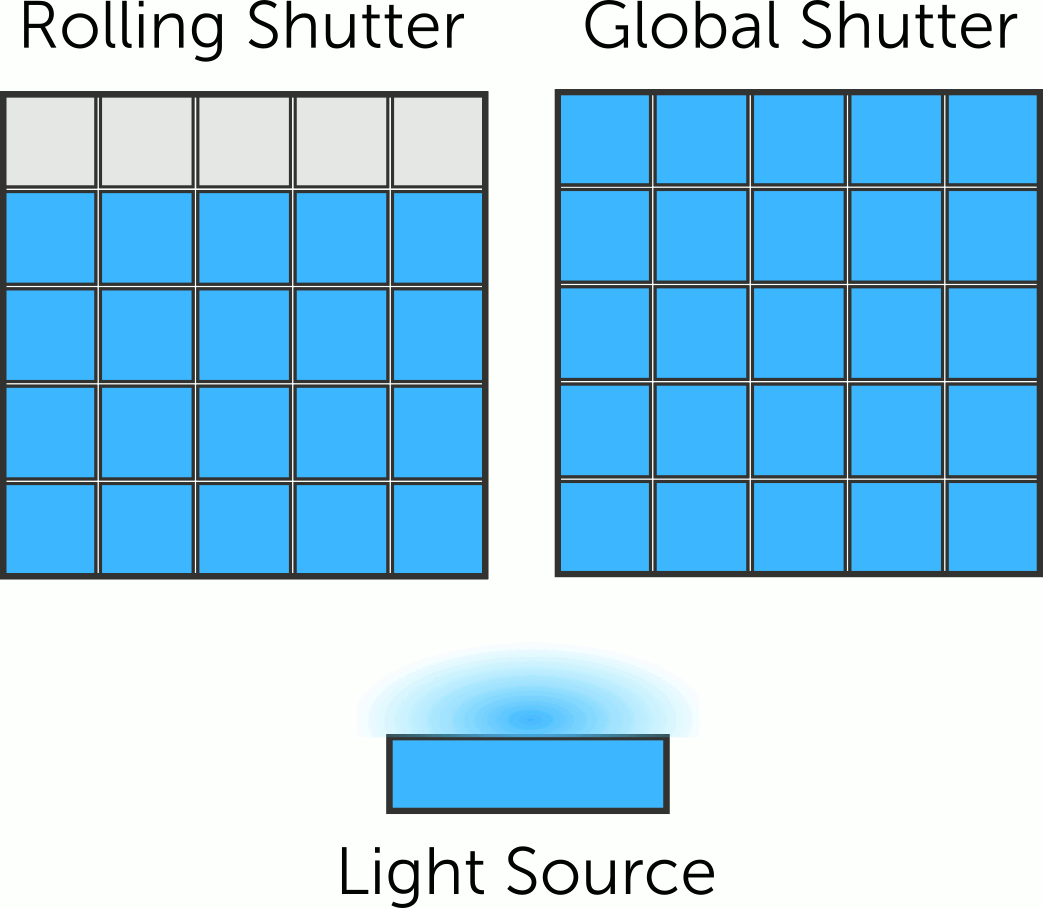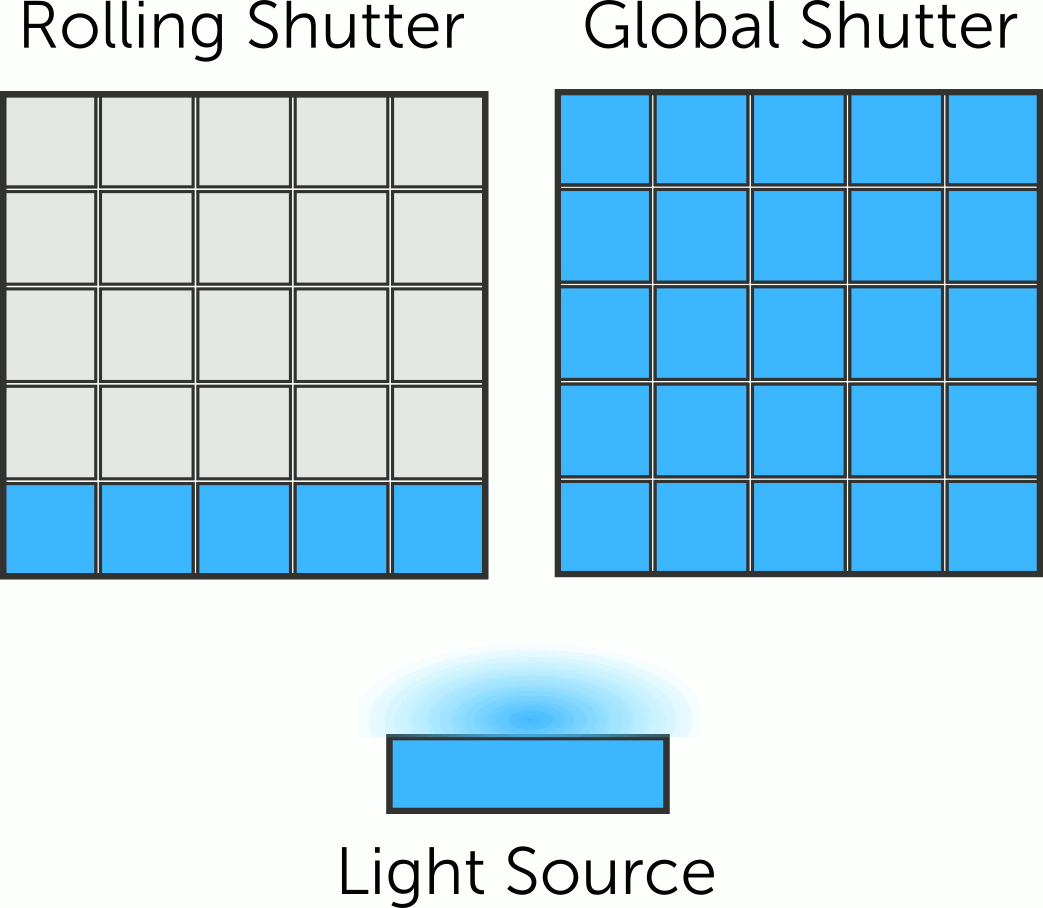
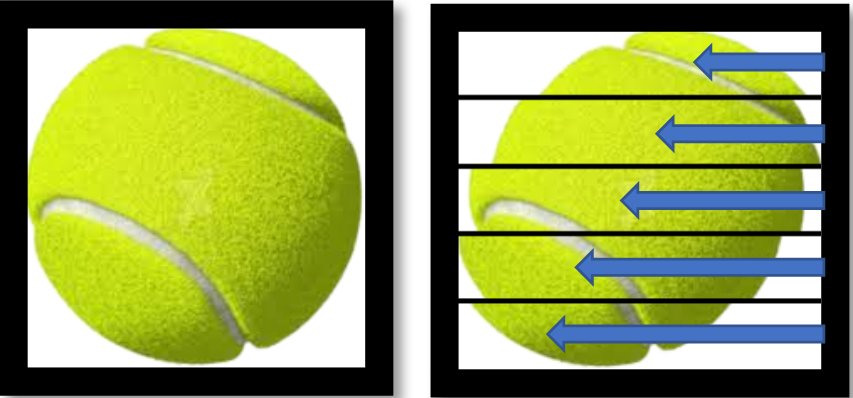
Since the rolling shutter captures different parts of the image at slightly different times, it can create motion blurriness. When there is an object moving at a very high speed, it may appear distorted or elongated due to the time difference in capturing different parts of the target. This is particularly noticeable in sports photography or when capturing moving vehicles.
A faster shutter speed reduces the sensor's exposure time to light, helping to minimize motion blur. However, even at high shutter speeds, rolling shutter distortion can still occur if the subject is moving extremely fast. In such cases, the most effective solution is to use a camera module equipped with a global shutter. For capturing high-speed motion accurately, we recommend trying our global shutter camera module.